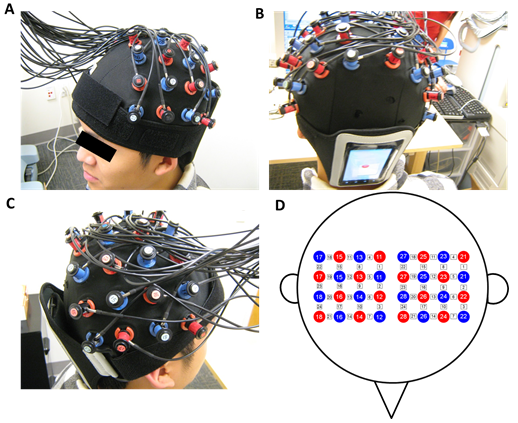
Is it possible to use a smartphone to measure head motion in a NIRS study? Is it reliable? After all, smartphones are so popular right now and everybody has it. It would make head motion measurement much more convenient than a traditional stand-alone accelerometer if the answers to the above questions are yes.
The good news is, the answers are YES!
In our recently published paper, we demonstrated that a NIRS researcher can easily attach a smartphone to a participant’s head, measure the motion data (3-D), export and analyze the data, and integrate with NIRS measurement.
The title of the paper is “Sensitivity of fNIRS measurement to head motion: An applied use of smartphones in the lab“. The full-text can be found here.
Abstract
Background
Powerful computing capabilities in small, easy to use hand-held devices have made smart technologies such as smartphones and tablets ubiquitous in today’s society. The capabilities of these devices provide scientists with many tools that can be used to improve the scientific method.
Method
Here, we demonstrate how smartphones may be used to quantify the sensitivity of functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) signal to head motion. By attaching a smartphone to participants’ heads during the fNIRS scan, we were able to capture data describing the degree of head motion.
Results
Our results demonstrate that data recorded from an off-the-shelf smartphone accelerometer may be used to identify correlations between head-movement and fNIRS signal change. Furthermore, our results identify correlations between the magnitudes of head-movement and signal artifact, as well as a relationship between the direction of head movement and the location of the resulting signal noise.
Conclusions
These data provide a valuable proof-of-concept for the use of off-the-shelf smart technologies in neuroimaging applications.
Keywords
- Near-infrared spectroscopy;
- fNIRS;
- smartphone;
- technology;
- neuroimaging;
- accelerometer